Under health and safety law employers are responsible for managing health and safety risks in their businesses. These roles assist parliamentarians, mop (s) act employees and finance to meet their duties under the whs act.

Find out more about the new laws, transitional arrangements and access copies of the whs act and regulations.
Roles and responsibilities of employers and employees under the whs legislation. Comply with any reasonable instructions, policies and procedure given by their employer, business or controller of the workplace. Ensure workers are safe when they use, handle, store or transport plant or substances. Worker or other person in the workplace.
Take reasonable care for the health and safety of others. Keep information and records relating to health. If you want to know what restrictions on.
The following provides a broad outline of how the law applies to employers. Duty to other people in the workplace. This document outlines the duties of employers, contractors and employees under the occupational health and safety act 2004.
In certain circumstances, where a mop(s) act employee is authorised by a parliamentarian to make decisions that affect the whole, or a substantial part of the parliamentarian’s representative work, the mop(s) act employee may also have the. Mop(s) act employees whs duties. How employers must comply with duties under the act to protect employees’ health and safety.
In western australia, the law requires your employer to provide a. While at work a worker must: Protect your own health and safety.
Provide a safe work environment. What a contractor is and their responsibilities to look after employees’ health and safety. Main responsibilities and duties under whs.
Make sure your employer has provided you with induction, training and instructions so you feel safe doing the work being asked of you. An officer’s duty is to exercise ‘due diligence’ to ensure their pcbu meets its duties to protect workers and other persons against harm to health and safety. Find out more about the new laws, transitional arrangements and access copies of the whs act and regulations.
To take reasonable care of your own health and safety. Duty to maintain the workplace and facilities. With these guidelines, employers have certain rights and responsibilities, which can be confusing for businesses to keep track of.
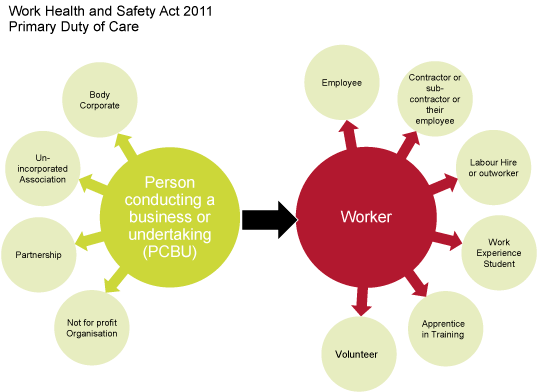
A person conducting a business or undertaking ( pcbu ), such as an employer. Take reasonable care to not adversely affect others’ health and safety. Consultation and worker representation under whs
Failure to comply with work health and safety legislation can result in civil and criminal penalties not to mention increases […] As an employer you have the main responsibility for the health and safety of everyone in your workplace, including visitors. The whs act created legislation and regulations to help increase workplace health and safety in australia.
These roles assist parliamentarians, mop (s) act employees and finance to meet their duties under the whs act. Workers including employees, contractors, subcontractors, labour hire employees, outworkers, apprentices or volunteers have a duty to: Keep your work area free of hazards.
Some practical ways of carrying out your duty of care responsibilities include ensuring: 11 rows employee / worker employer. Provide all workers, including managers and.
It is an employer�s duty to protect the health, safety and welfare of. More specifically, in relation to a section 28 duty owed by a worker: Officer must ensure that the pcbu has in place.
Your most important responsibilities as an employee are: You should report to mom if you notice. You have duties under whs laws to keep people in the workplace safe if you’re:
Some business operations are restricted under state or territory government public health directions. If possible to avoid wearing jewellery or loose clothing if operating machinery. As an employer or business owner, your legal responsibility is known as your primary duty of care in the work health and safety act 2011.
An employee of a labour hire company. In summary, the health and safety at work act 1974 outlines the legal duties that employers have to protect the health, safety and welfare at work of all of their employees. To minimise the risks to your health and safety:
In broad terms, a worker’s duties under section 28 reciprocate the protections they receive under duties like the primary duty of care in section 19(1). Take reasonable care for their own health and safety while at work. A person can have more than one duty under the model whs laws.
If you have long hair, or wear a headscarf, make sure it�s tucked out of the way as it could get caught in machinery. A worker who does not comply with a duty imposed on him/her under section 28 commits an offence. All parliamentarians and mop (s) act employees have duties under commonwealth whs legislation.
Ensure safe use, handling and storage of machinery, structures and substances. Provide and maintain a safe means of access to and from the workplace that is safe for workers. Learn about your duties under the whs act.
Monitor your employees’ health (for example, provide hearing tests if they are exposed to high noise levels). To meet your duty of care, you must: Take reasonable care for their own health and safety.
Provide adequate facilities for the welfare of workers at work and appropriate health, medical and first aid services. Under health and safety law employers are responsible for managing health and safety risks in their businesses. Information about wa’s new work health and safety (whs) laws.
Duty to provide information, training, instruction and supervision. Monitor conditions at the workplace under your management and control. Give your employees information about workplace health and safety in appropriate languages.
All workers are responsible for protecting their own health and safety at work. Every mop(s) act employee has the duties of a worker under the whs act. To ensure that the pcbu has, and implements, processes for complying with any duty or obligation the pcbu has under the whs act.