The house of representatives comprises congressmen and congresswomen elected to represent and serve the interests of their particular district. Any member can introduce a proposed law (bill) but most are introduced by the government.

To become law, bills must be passed by both the house of representatives and the senate.
Roles and responsibilities of the house of representatives australia. At first glance political representation in a liberal democracy such as australia is a straightforward concept: They are elected by their party to lead their team, and have the power to choose other. The house is made up of 151 members.
They may start in either house but the majority of bills are introduced in the house of representatives. In addition the speaker has certain ex officio functions. This diagram illustrates the role of the house of representatives.
Any member can introduce a proposed law (bill) but most are introduced by the government. The ministry is responsible for making and defending government decisions and legislative proposals. The house is also known as the lower house.
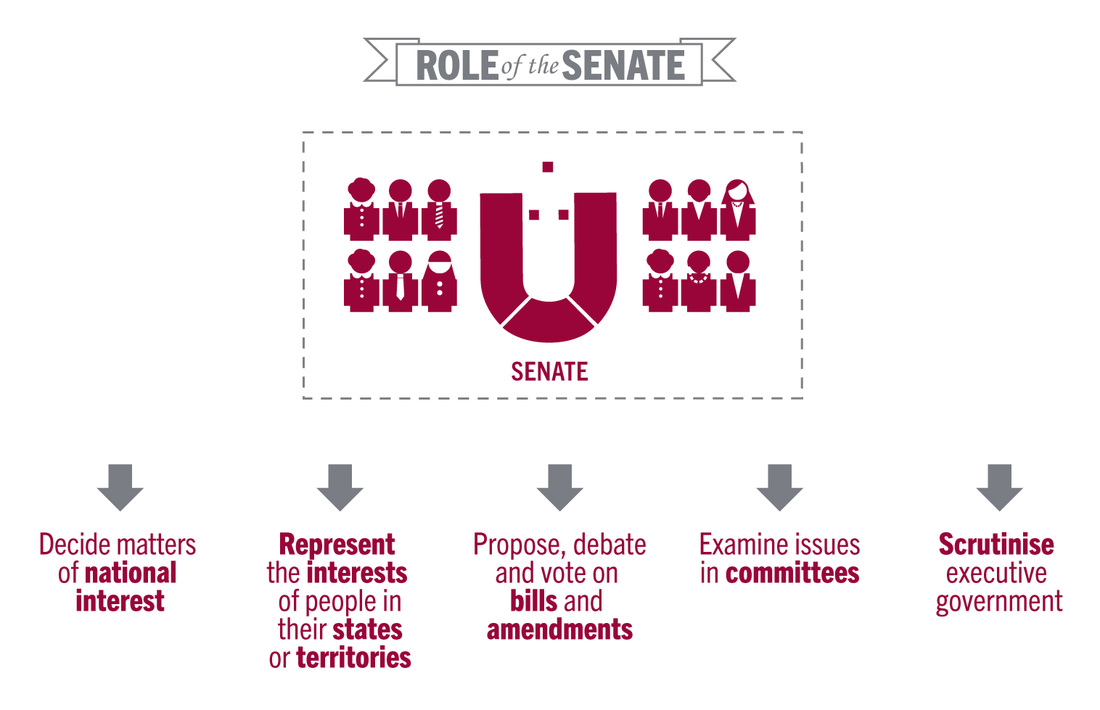
Proposes, debates and votes of bills and amendments; Represents the interests of people in their electorates; The house of representatives comprises congressmen and congresswomen elected to represent and serve the interests of their particular district.
Members often represent political parties. Members of the house are elected by the people of australia. Representing australia overseas, through key spokespersons such as the prime minister and the minister for foreign affairs.
The premier leads and coordinates the work of the ministers, having greater authority over all aspects of the cabinet and government’s actions than any other minister. It is the house in which the australian government is formed and has an important role representing the views of australians and making laws for australia. The house of representatives is part of the australian parliament.
Three levels of government in australia. Since the late 1960s the house of representatives has sought to strengthen its ability to scrutinise the actions and policies of government, mainly through the creation of committees. Decides matters of national interest;
Vienna convention on diplomatic relations Collectively, these duties mean that members of parliament have roles as parliamentarians, as representatives of their constituents (electors) and generally as members of their political party. To become law, bills must be passed by both the house of representatives and the senate.
These representatives are responsible for voting on as well as proposing, bills, resolutions and amendments. The leader of the australian government is the prime minister, who is a member of the house of representatives. However, government proposals are subject to parliamentary scrutiny which is essential in the concept of responsible government.
If a representative truly feels that a committee’s decision or legislation will have a negative effect, they must vote their conscience. Since it is the responsibility of the house of representatives to represent public interest. To become law, bills must be passed by both the house of.
Any member can introduce a proposed law (bill) but most are introduced by the government. This is the institution that approves the national budget and verifies the assignments that are made of it. It includes the roles and responsibilities of each level.
There are few important decisions made by the parliament which are not first considered by the government. The term of members of the house of representatives is a maximum of three years from the date of the first sitting of the house, but on only one. About every three years at a national level there is an election where citizens in defined geographic areas (be it a local electorate or a state/territory) choose from a range of candidates—themselves citizens living in (or near) that.
House representatives must always vote the way they truly feel no matter what others want them to do. Australia has three levels of government that work together to provide us with the services we need. The majority of members belong to a political party and contribute to the views and policies of that party.
Is where government is formed; State and territory parliaments, in each state and territory capital city. As a general point of principle the speaker’s authority is that which is derived from the house, and the foremost duty is to the.
Representatives need to conduct themselves in. It is this role which probably attracts the most publicity but, at the same time, it is the one which is probably least demanding of a member’s time. The speaker’s powers, functions and duties may be categorised as constitutional, traditional and ceremonial, statutory, procedural and administrative.
The house of representatives is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of australia, the upper house being the senate.its composition and powers are established in chapter i of the constitution of australia. Rep’s role as a representation of ric and of themselves: Likewise, it is before the house of representatives that the accounts of that budget are rendered and the extraordinary expenses are justified, if they exist.
Makes laws —the house�s central function and the one which takes up most of its time is the consideration and passing of new laws and amendments or changes to existing laws.