Powers are divided between the union and state governments. Supreme court is the federal court of india, india being a federation;
The supreme court of india is the highest judicial court and the final court of appeal under the constitution of india, the highest constitutional court, with the power of judicial review.;
What are the main roles of the supreme court of india. The supreme court of india composition, powers and functions. Thus the supreme court also functions as a court of record. With this purpose in view, the supreme court occupies the highest place in our unitary judicial system.
The judges of the supreme court should possess the following qualifications: Therefore, the supreme court is the guardian of our constitution. The role and functions of the supreme court in our judicial and political system may be discussed under the following heads:
The supreme court being a court of appeal hears appeals against the judgements of the lower courts. The judges sit in benches of 2 or 3 is called a division bench. The primary duty of the supreme court is to ascertain whether the laws are executed and obeyed properly and to see to it that no person is deprived of justice in any court of law.
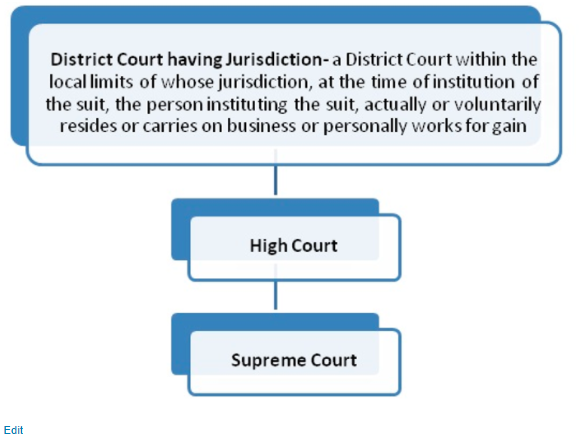
India is a federal state and has a single and unified judicial system with three tier structure, i.e. Powers are divided between the union and state governments. It also works as intermediary in the issues.
The primary duty of the supreme court is to ascertain whether the laws are executed and obeyed properly and to see to it that no person is deprived of justice in any court of law. The supreme court of india (iast: With this purpose in view, the supreme court occupies the highest place in our unitary judicial system.
The judges sit in benches of 5 or more is called a constitutional bench at. Supreme court is the federal court of india, india being a federation; It hears and gives rulings on both civil and criminal cases as well as those concerning the constitution of india.
Let us discuss the role of supreme court. The supreme court, at the apex of the indian judiciary, is the highest authority to interpret and uphold the constitution of india, to protect the rights and liberties of the citizens, and to abide by the values of law. Supreme court, high courts and subordinate courts.;
It means that all such cases begin or originate in the supreme court, only. (ii) appeals in civil matters; The supreme court of india is the highest judicial court and the final court of appeal under the constitution of india, the highest constitutional court, with the power of judicial review.;
The supreme court has the power to appoint its officers and servants. The supreme court has three types of jurisdictions namely original, appellate and advisory. “the word “environment” relates to.
Brief history of the supreme court of india B) it acts as an institution where issues from the different governmental bodies, central government, and the state government matters are resolved. This court gives legal advice to the president of india on matters of constitutional or legal importance.
Bhārat kē ucchatama nyāyālaya) is the supreme judicial authority of india and is the highest court of the republic of india under the constitution.it is the most senior constitutional court, has the final decision in all legal matters, and also has the power of judicial review.the chief justice of india is the head and chief judge of the supreme court. Composition of the supreme court. The supreme court of india has defined its own powers in the famous case of a.
The following are the supreme court functions: The supreme court of india is neither as powerful as the american judiciary nor as powerless as the british judiciary. Article 124 (1) of the constitution of india says that there shall be one supreme court in india, which shall consist of the chief justice of india, and other 34 judges including the chief justice of india.
If the government passes any law against the constitution, the supreme court declares it unconstitutional. The qualifications of the judges. Though the person has to be qualified for the job.
The primary duty of the supreme court is to ascertain whether the laws are executed and obeyed properly and to see to it that no person is deprived of justice in any court of law. Some of important functions of supreme court are. Public interest litigation has play a very crucial role in the process of development as all the decisions of supreme court resulted in it’s formation.
The supreme court is the head of the entire judicial system which functions as the sentinel and defender of the fundamental rights. The decisions and decrees issued by the supreme court become case law and are referred to by lawyers in their pleadings in similar situations. A) the sc gives the final verdict against an appeal from the other subsidiary courts i.e., high courts.
It has been marked as the most strong sword for the preservationist and conservationist. Indian judiciary is very well formed with great interweaving. Pil is a tool for judiciary to prevent the environment.
While announcing a new initiative we welcome you to the new website of the supreme court of india (sci.gov.in / supremecourt.gov.in). C) as per article 141 of the constitution. (iv) appeals in special leave.
There are certain cases which fall within the exclusive jurisdiction of the supreme court. For example, chief justice of india or the other supreme court judges is appointed by it to carry out its functions. (iii) appeals in criminal matters;
Supreme court under article 129 has the power to punish a person if found guilty of contempt of court. The supreme court is the court of record since the decisions made by sc are of evidentiary value. Attempt has been made, as far as possible, to ensure its.
It held, “in india the position of judiciary is somewhere between the courts of england and the united states”. It also means that such cases cannot be initiated in any other. The judicial system is same for whole india.
The supreme court is responsible for ensuring that the high courts and the subordinate courts function efficiently and effectively. Attempt has been made, as far as possible, to ensure its. Article 124 (1) and amendment act of 2008 states that there shall be a supreme court of india consisting of a chief justice of india (cji) and 34 judges including.